Continuing Part 1 with a 2024 rodent healthspan and lifespan study:
“We investigated the effects of daily oral supplementation of ergothioneine (ERGO) dissolved in drinking water on lifespan, frailty, and cognitive impairment in male mice from 7 weeks of age to the end of their lives. Ingestion of 4 ~ 5 mg/kg/day of ERGO remarkably extended the lifespan of male mice.
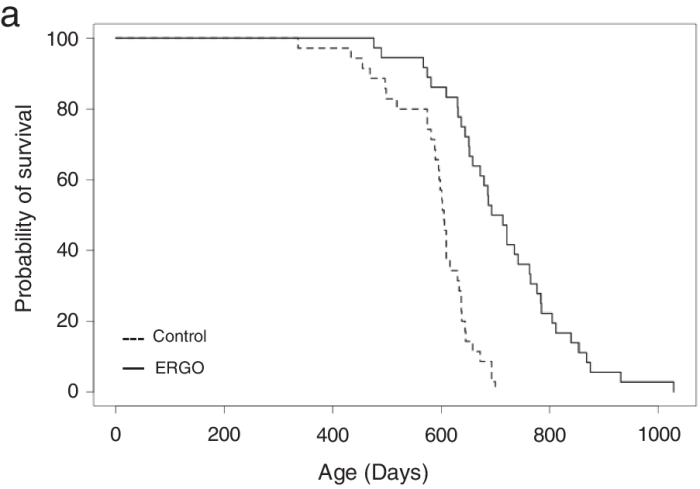
The ERGO group showed significantly lower age-related declines in weight, fat mass, and average and maximum movement velocities at 88 weeks of age. This was compatible with dramatic suppression by ERGO of age-related increments in plasma biomarkers. ERGO also rescued age-related impairments in learning and memory ability.
Ingestion of ERGO may promote longevity and healthy aging in male mice, possibly through multiple biological mechanisms.”
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11357-024-01111-5 “Ergothioneine promotes longevity and healthy aging in male mice”
Subjects’ plasma ergothioneine levels of an estimated 4 ~ 5 mg/kg daily dose were:
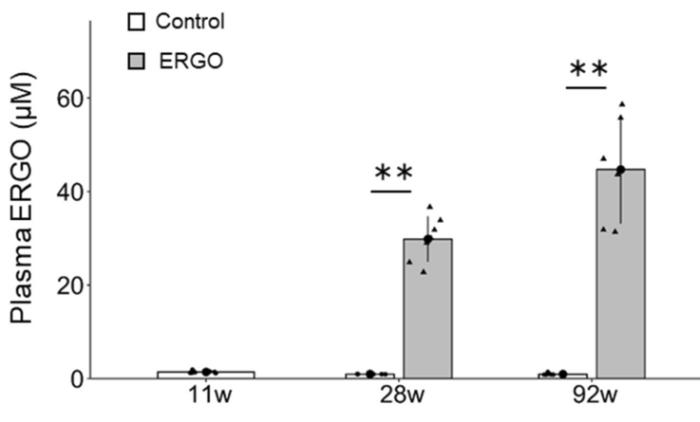
A human equivalent daily dose is an estimated 22 mg to 28 mg (4 or 5 mg x .081 x 70 kg).
The third paper in Part 1 cited a 2017 clinical trial that provided 5 mg and 25 mg ergothioneine doses for 7 days, resulting in these plasma ergothioneine levels:
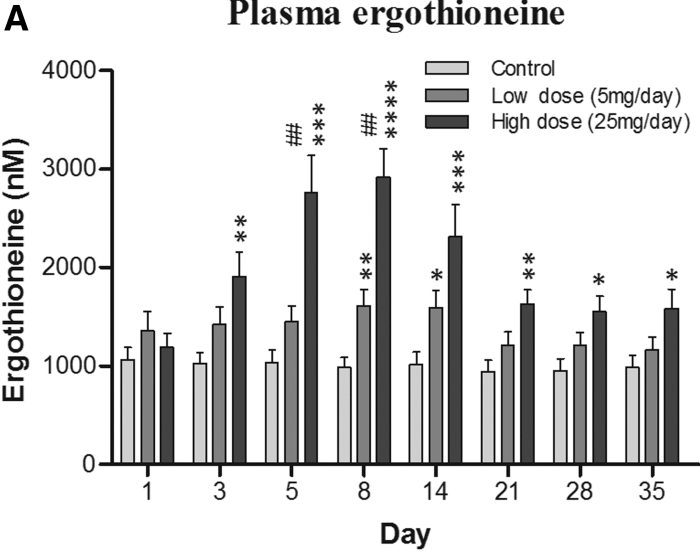
The first paper of Part 1 referenced a 2020 human study where the dose was 5 mg/day for 12 weeks, but I don’t have access to it. It’s unclear whether humans could continually raise ergothioneine levels by daily consumption throughout our lives as did this rodent study.
A 2024 paper reviewed the importance of ergothioneine to humans:
“We propose that the diet-derived compound ergothioneine (ET) is an important nutrient in the human body, especially for maintenance of normal brain function, and that low body ET levels predispose humans to significantly increased risks of neurodegenerative and possibly other age-related diseases.
Work by multiple groups has established that low ET levels in humans are associated not only with cognitive impairment/AD but also with other age-related conditions, including frailty, Parkinson’s disease, vascular dementia, chronic renal disease, cardiovascular disease, and macular degeneration. Low ET levels also correlate with increased risk of developing preeclampsia in pregnant women [53].
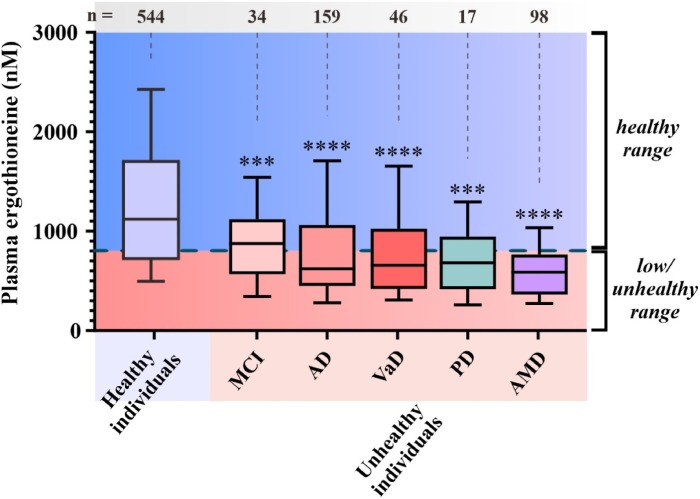
Plasma ET levels from healthy (age-matched) vs unhealthy individuals in Singapore – Mild cognitive impairment (MCI); Alzheimer’s disease (AD); vascular dementia (VaD); Parkinson’s disease (PD); age-related macular degeneration (AMD):
- Does low ET cause or contribute to age-related neurodegeneration, or
- Does disease cause low ET, or
- Low ET and increased disease risk are both caused by something else, as yet unidentified?
Prevention of neurodegeneration is especially important, since by the time dementia is usually diagnosed damage to the brain is extensive and likely irreversible.”
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0891584924001357 “Are age-related neurodegenerative diseases caused by a lack of the diet-derived compound ergothioneine?”
Whether or not the healthy individuals ate mushrooms daily in the above graphic was lost while conglomerating multiple studies.
Note that scales of the above two human graphics are a thousand times smaller than the above rodent graphic. I thought that maybe the rodent study made a plasma ergothioneine calculation error, but didn’t see one in the provided Supplementary data.
Reference 53 of the second paper is a 2023 human study:
“We analysed early pregnancy samples from a cohort of 432 first time mothers. Of these 432 women, 97 went on to develop pre-term or term pre-eclampsia (PE).
If a threshold was set at the 90th percentile of the reference range in the control population (≥462 ng/ml), only one of these 97 women (1%) developed PE, versus 96/397 (24.2%) whose ergothioneine level was below this threshold. One possible interpretation of these findings, consistent with previous experiments in a reduced uterine perfusion model in rats, is that ergothioneine may indeed prove protective against PE in humans.”
https://portlandpress.com/bioscirep/article/43/7/BSR20230160/233119/Relationship-between-the-concentration-of “Relationship between the concentration of ergothioneine in plasma and the likelihood of developing pre-eclampsia”
Eyeballing the Healthy individuals in the above graphic, none of those 544 people were below this study’s 462 ng threshold.
A 2023 companion article analyzed the third paper’s unusual findings:
“These results suggest that there might be a dichotomized association between ergothioneine concentrations and preeclampsia; and only a high ergothioneine level over 90th percentile of the control population could be protective against preeclampsia.
Univariable results showed that ergothioneine had a significant non-linear association with preeclampsia and it would start to offer protective effect from 300 ng/ml onward. Analysis also confirmed that body mass index was significantly associated with an increased risk of preeclampsia.
A large observational study could strengthen the causal association between ergothioneine and preeclampsia. If confirmed, a randomized controlled trial (RCT) assessing whether ergothioneine supplementation can reduce risk of preeclampsia will be imminently feasible. Ideally, such RCT should compare placebo with a range of different doses of ergothioneine to identify the best or minimal effective dose, given its good safety records, including in pregnancy, with a no-observed-adverse-effect level (NOAEL) of 800 mg/kg body weight per day.”
https://portlandpress.com/bioscirep/article/43/8/BSR20231076/233395/Dose-related-relationship-between-ergothioneine “Dose-related relationship between ergothioneine concentrations and risk of preeclampsia”
My daily mushroom ergothioneine dose is around 7 mg, and I weigh about 70 kg. I don’t think a daily 800 mg/kg ergothioneine dose would be desirable for anybody, regardless of what experts say.
How many times have public health employees been wrong this decade? Would you bet your or your child’s health on their advice?