Two preprint studies looked at making transcriptional aging clocks using Nrf2 activators. Let’s start with a 2025 nematode study that used constant exposure to sulforaphane at different concentrations:
“To explore the potential of sulforaphane as a candidate natural compound for promoting longevity more generally, we tested the dose and age-specific effects of sulforaphane on C. elegans longevity, finding that it can extend lifespan by more than 50% at the most efficacious doses, but that treatment must be initiated early in life to be effective. We then created a novel, gene-specific, transcriptional aging clock, which demonstrated that sulforaphane-treated individuals exhibited a “transcriptional age” that was approximately four days younger than age-matched controls, representing a nearly 20% reduction in biological age.
The clearest transcriptional responses were detoxification pathways, which, together with the shape of the dose-response curve, indicates a likely hormetic response to sulforaphane. The hormetic, stress-pathway inducing properties of sulforaphane may indicate that many beneficial dietary supplements work in a fairly generic fashion as mild toxins rather than being driven by the biochemical properties of the compounds themselves (e.g., as antioxidants).

These results support the idea that robust longevity-extending interventions can act via global effects across the organism, as revealed by systems level changes in gene expression.”
https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2025.05.11.653363v1 “The broccoli derivative sulforaphane extends lifespan by slowing the transcriptional aging clock”
There are difficulties in researchers translating nematode studies to mammals and humans. Nematodes lack a homolog to the Keap1 protein, which is sulforaphane’s main mammalian target to activate Nrf2.
A 2024 study developed various mammalian epigenetic clocks:
“A unified transcriptomic model of mortality that encompasses both aging and various models of lifespan-shortening and longevity interventions (i.e., mortality clocks) has been lacking. We conducted an RNA-seq analysis of mice subjected to 20 compound treatments in the Interventions Testing Program (ITP).
We sequenced the transcriptomes of a large cohort of ITP mice subjected to various neutral and longevity interventions, expanded the dataset with publicly available gene expression data representing organs of mice and rats across various strains and lifespan-regulating interventions, connected these models with survival data, and performed a meta-analysis of aggregated 4,539 rodent samples, which allowed us to identify multi-tissue transcriptomic signatures of aging, mortality rate, and maximum lifespan.
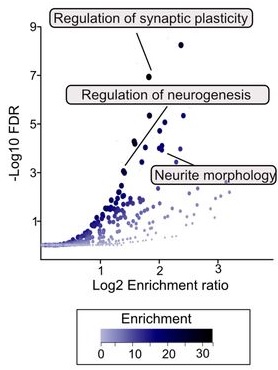
Aging and mortality were characterized by upregulation of genes involved in inflammation, complement cascade, apoptosis, and p53 pathway, while oxidative phosphorylation, fatty acid metabolism, and mitochondrial translation were negatively associated with mortality, both before and after adjustment for age.
Utilizing the aggregated dataset, we developed rodent multi-tissue transcriptomic clocks of chronological age, lifespan-adjusted age, and mortality. While the chronological clock could distinguish the effect of detrimental genetic and dietary models, it did not show a decrease in biological age in response to longevity interventions. In contrast, clocks of lifespan-adjusted age and mortality both captured aging-associated dynamics and correctly predicted the effect of lifespan-shortening and extending interventions.
Transcriptomic biomarkers developed in this study provide an opportunity to identify interventions promoting or counteracting molecular mechanisms of mortality, and characterize specific targets associated with their effects at the level of cell types, intracellular functional components, and individual genes. Our study underscores the complexity of aging and mortality mechanisms, the interplay between various processes involved, and the clear potential for developing therapies to extend healthspan and lifespan.”
https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2024.07.04.601982v1.full “Transcriptomic Hallmarks of Mortality Reveal Universal and Specific Mechanisms of Aging, Chronic Disease, and Rejuvenation”
This second study’s references included an ITP study curated in Astaxanthin and aging, which stated:
“Despite the fact that the average diet contained 1840 ppm astaxanthin (only 46% of the target), median lifespans of male UM-HET3 mice were significantly improved. Amounts of dimethyl fumarate (DMF) in the diet averaged 35% of the target dose, which may explain the absence of lifespan effects.”
So screw-ups in making both astaxanthin and DMF mouse chows ended up with study data that didn’t measure the full lifespan impacts of activating transcription factor Nrf2. I’ll assert that such faulty data may have deviated this second study by downplaying Nrf2 activation’s impact on aging, chronic disease, and rejuvenation.
Sponsors may be less likely to be presented sulforaphane and other Nrf2 activator candidates for future aging and chronic disease studies as this first study suggests, thinking that these have already been studied in mammals. Well, maybe these compounds haven’t been accurately studied. There’s no effective way to fix a rodent study’s missing DMF Nrf2 data and faulty astaxanthin Nrf2 data to train an epigenetic clock in this second study.
I could be wrong about this second study using faulty astaxanthin Nrf2 data. It was cited as Reference 27 in the Introduction as an ITP study, but not specifically cited in the Method section. I don’t know how findings such as one of Nrf2’s target genes (“Remarkably, one of the top genes positively associated with maximum lifespan and negatively associated with chronological age and expected mortality was Gpx1, encoding the selenoprotein glutathione peroxidase 1″) and a Nrf2 specific pathway (Phase II) (“Pathways positively associated with lifespan and negatively with mortality, both before and after adjustment for age, included..xenobiotic metabolism..”) were made without Reference 27. Neither of the above studies has been peer reviewed yet.