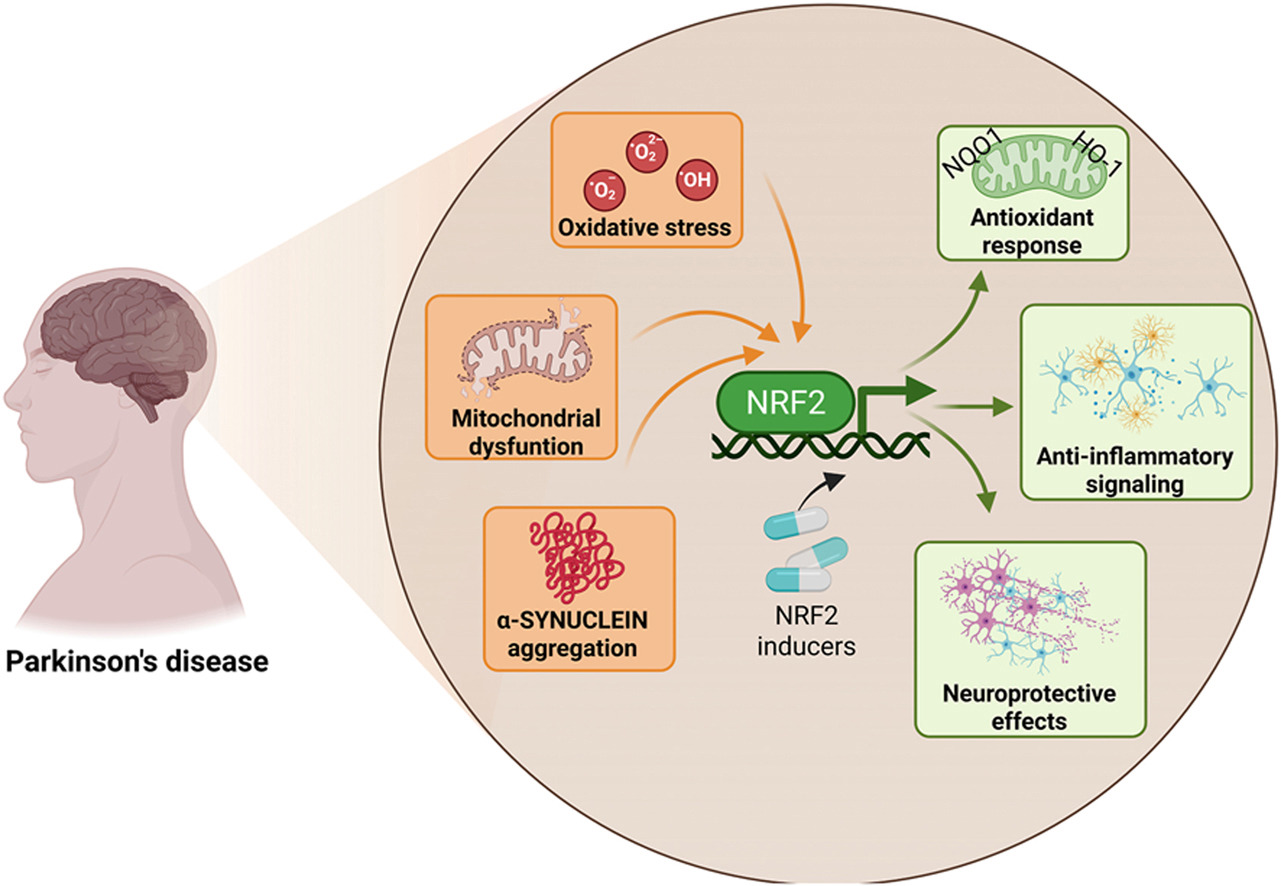
Three papers on myelin and oligodendrocytes, starting with a 2023 review:
“Myelin is the spiral ensheathment of axons by a lipid and cholesterol-rich glial cell membrane that reduces capacitance and increases resistance of the axonal membrane. Axonal myelination speeds up nerve conduction velocity as a function of axon diameter.
While myelination proceeds rapidly after birth in the peripheral nervous system, central myelination is a spatially and temporally more regulated process. Ongoing myelination of the human brain has been documented at up to 40 years of age. This late myelination in the adult cortex is followed by exhaustion of oligodendrocyte precursor cells (OPC) with senescence and a gradual loss of myelin integrity in the aging brain.
The brain is well known for its high energy demands, specifically in gray matter areas. In white matter tracts, energy consumption is lower. Myelination poses a unique challenge for axonal energy generation where myelin sheaths cover more than 95% of the axonal surface areas.
Oligodendrocytes help support axonal integrity. Oligodendrocytes survive well in the absence of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation, and without signs of myelin loss, cell death, neurodegeneration or secondary inflammation.
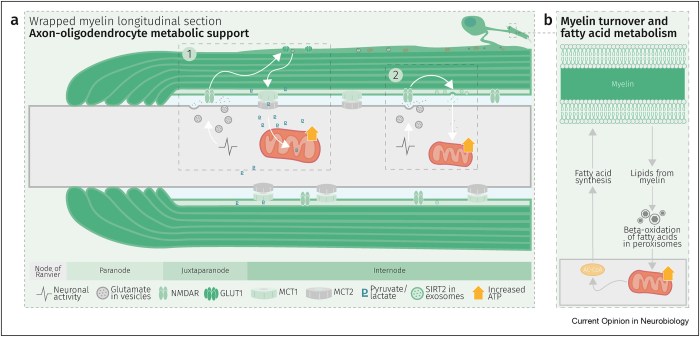
Glycolysis products of oligodendroglial origin are readily metabolized in axonal mitochondria. Oligodendroglial metabolic support is critical for larger and faster-spiking myelinated axons that also have a higher density of mitochondria. An essential requirement for the direct transfer of energy-rich metabolites from oligodendrocytes to the myelinated axonal compartment is ‘myelinic channels’ within the myelin sheath.
Interactions of oligodendrocytes and myelin with the underlying axon are complex and exceed the transfer of energy-rich metabolites. Continuous turnover of myelin membranes by lipid degradation and fatty acid beta-oxidation in mitochondria and peroxisomes leads to recycling of acetate residues by fatty acid synthesis and membrane biogenesis.
In human multiple sclerosis (MS) and its animal model myelin oligodendrocyte glycoprotein-experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (MOG-EAE), acute inflammatory demyelination is followed by axonal degeneration in lesion sites that is mechanistically not fully understood. It is widely thought that demyelination and the lack of an axon-protective myelin sheath in the presence of numerous inflammatory mediators are the main causes of axon loss.
But unprotected axons improve rather than worsen the overall clinical phenotype of EAE mice which exhibited the same degree of autoimmunity. Thus, ‘bad myelin is worse than no myelin’ because MS-relevant myelin injuries perturb the integrity of myelinic channels and metabolic support.
Dysfunctional or injured oligodendrocytes that do not allow for compensation by any other cell types turn the affected myelin ensheathment into a burden of the underlying axonal energy metabolism, which causes irreversible axon loss. Any loss of myelin integrity, as seen acutely in demyelinating disorders or more gradually in the aging brain, becomes a risk factor for irreversible neurodegeneration.”
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0959438823001071 “Expanding the function of oligodendrocytes to brain energy metabolism”
A 2024 review focused on myelin and oligodendrocyte plasticity:
“This review summarizes our current understanding of how myelin is generated, how its function is dynamically regulated, and how oligodendrocytes support the long-term integrity of myelinated axons.
Apart from its unique ultrastructure, there are several other exceptional features of myelin. One is certainly its molecular composition. Another is its extraordinary stability. This was compellingly illustrated when 5000-year-old myelin with almost intact ultrastructure was dissected from a Tyrolean Ice Man.
Myelin is a stable system in contrast to most membranes. However, myelin is compartmentalized into structurally and biochemically distinct domains. Noncompacted regions are much more dynamic and metabolically active than tightly compacted regions that lack direct access to the membrane trafficking machinery of oligodendrocytes.
The underlying molecular basis for stability of myelin is likely its lipid composition with high levels of saturated, long chain fatty acids, together with an enrichment of glycosphingolipids (∼20% molar percentage of total lipids) and cholesterol (∼40% of molar percentage of total lipids). In addition, myelin comprises a high proportion of plasmalogens (ether lipids) with saturated long-chain fatty acids. In fact, ∼20% of the fatty acids in myelin have hydrocarbon chains longer than 18 carbon atoms (∼1% in the gray matter) and only ∼6% of the fatty acids are polyunsaturated (∼20% in gray matter).
With maturation of oligodendrocytes, the plasma membrane undergoes major transformations of its structure. Whereas OPCs are covered by a dense layer of large and negatively charged self-repulsive oligosaccharides, compacted myelin of fully matured oligodendrocytes lacks most of these glycoprotein and complex glycolipids.
Schematic depiction of an oligodendrocyte that takes up blood-derived glucose and delivers glycolysis products (pyruvate/lactate) via monocarboxylate transporters (MCT1 and MCT2) to myelinated axons. Oligodendrocytes and myelin membranes are also coupled by gap junctions to astrocytes, and thus indirectly to the blood–brain barrier.

Adaptive myelination refers to dynamic events in oligodendroglia driven by extrinsic factors such as experience or neuronal activity, which subsequently induces changes in circuit structure and function. Understanding how these adaptive changes in neuron-oligodendroglia interactions impact brain function remains a pressing question for the field.
Transient social isolation during adulthood results in chromatin and myelin changes, but does not induce consequent behavioral alterations. When mice undergo a social isolation paradigm during early life development, they similarly exhibit deficits in prefrontal cortex function and myelination, but these deficiencies do not recover with social reintroduction. This implicates a critical period for social deprivation effects on myelin dynamics. Experience-dependent changes in myelin dynamics may depend on not only the age, brain region, and cell type studied, but also the specific myelin structural change assessed.
Local synaptic neurotransmitter release along an axon not only affects the number of OPCs and oligodendrocytes associated with that axon and local synthesis of myelin proteins, but also drives preferential selection of active axons for myelination over the ensheathment of electrically silenced neighboring axons. Neuronal activity–induced plasticity may preferentially impact brain regions that remain incompletely myelinated compared to more fully myelinated tracts.
Whereas the myelin sheath has been regarded for a long time as an inert insulating structure, it has now become clear that myelin is metabolically active with cytoplasmic-rich pathways, myelinic channels, for movement of macromolecules into the periaxonal space. The myelin sheath and its subjacent axon need to be regarded as one functional unit, which are not only morphological but also metabolically coupled.”
https://cshperspectives.cshlp.org/content/early/2024/04/15/cshperspect.a041359 “Oligodendrocytes: Myelination, Plasticity, and Axonal Support” (not freely available) Thanks to Dr. Klaus-Armin Nave for providing a copy.
A 2024 rodent study investigated oligodendrocyte precursor cell transcriptional and epigenetic changes:
“We used single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq), single-cell ATAC sequencing (scATAC-seq), and single-cell spatial transcriptomics to characterize murine cortical OPCs throughout postnatal life. One group (active, or actOPCs) is metabolically active and enriched in white matter. The second (homeostatic, or hOPCs) is less active, enriched in gray matter, and predicted to derive from actOPCs. Relative to developing OPCs, both actOPCs and hOPCs are less active metabolically and have less open chromatin.
In adulthood, these two groups are transcriptionally but not epigenetically distinct, indicating that they may represent different states of the same OPC population. If that is the case, then one model is that the parenchymal environment maintains adult OPCs within an hOPC state, whereas those OPCs recruited into white matter or exposed to demyelinated axons may transition toward an actOPC state in preparation for making new oligodendrocytes. We do not yet know the functional ramifications of these differences, but this finding has clear implications for the development of therapeutic strategies for adult remyelination.

Another finding is that developing but not adult actOPC chromatin is preferentially open for binding motifs associated with neural stem cells, transit-amplifying precursors, and neurogenesis. Although this may simply reflect their origin as the immediate progeny of neonatal neural precursor cells, it may also explain why developing but not adult OPCs have the capacity to make neurons in culture.
If we could, at least in part, reverse the global chromatin shutdown that occurs between development and adulthood, then perhaps adult OPCs may reacquire the ability to make neurons or become better able to generate new oligodendrocytes for remyelination.”
https://www.cell.com/stem-cell-reports/fulltext/S2213-6711(24)00077-8 “Single-cell approaches define two groups of mammalian oligodendrocyte precursor cells and their evolution over developmental time”
Continued in Part 2.