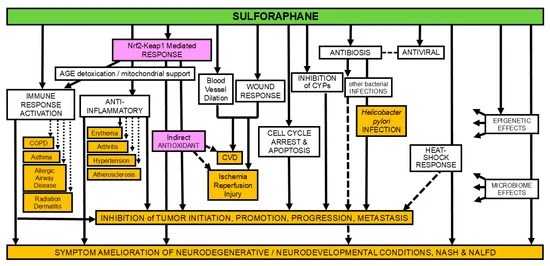
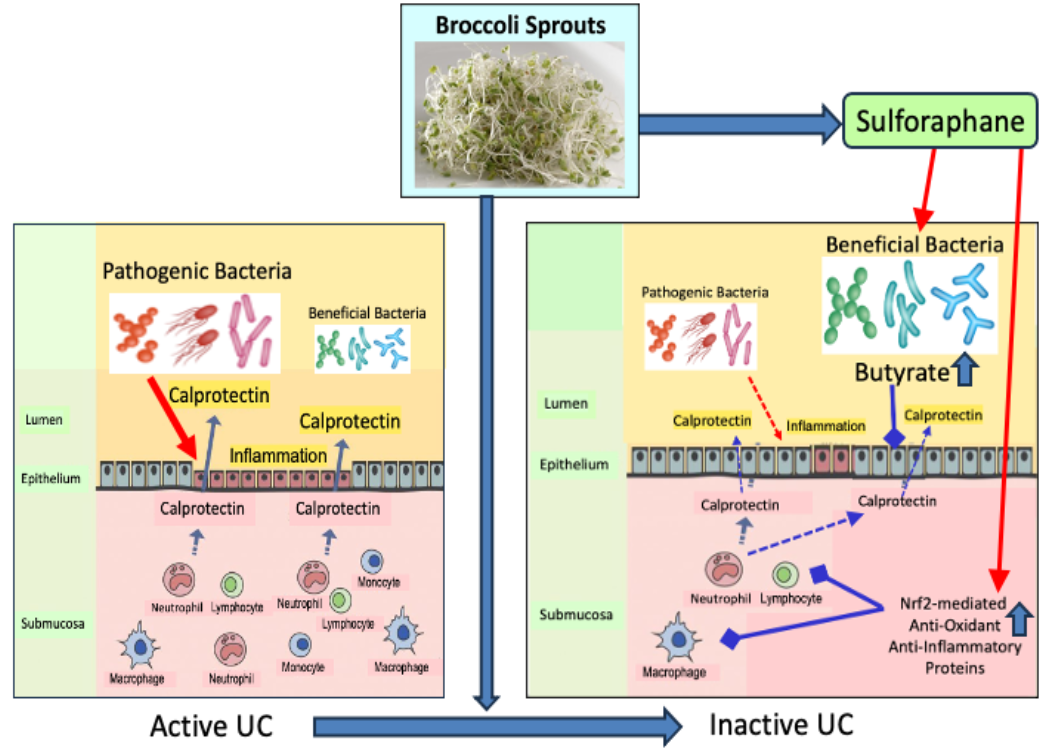
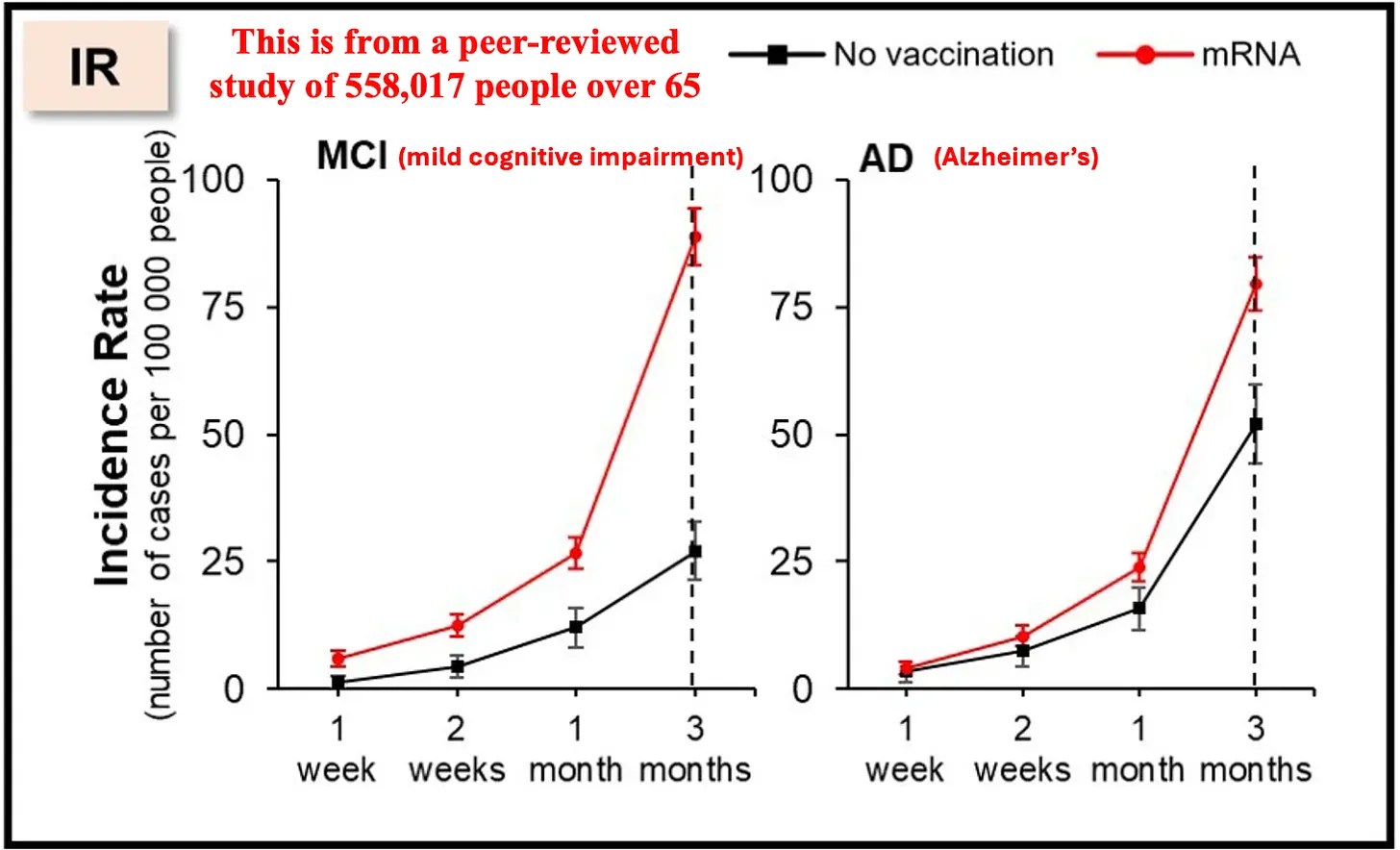
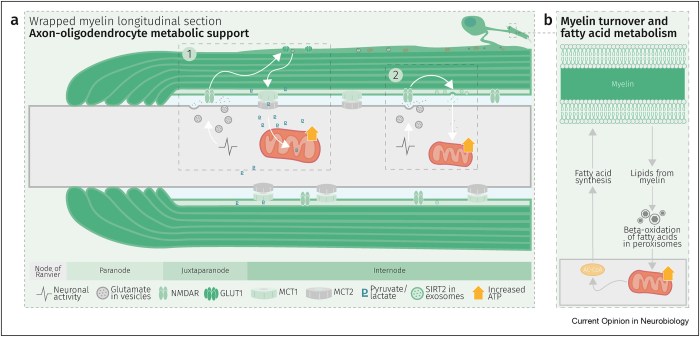
Three papers continue Polyphenol Nrf2 activators themes starting with a 2025 review of chlorogenic acid:
“Chlorogenic acid may comprise between 70 and 350 mg per cup of coffee. Chlorogenic acid can reduce reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels via the upregulation of antioxidant enzymes, decreasing oxidative stress/damage due to the action of adaptive hormetic mechanisms. There is also a substantial literature of hormetic dose responses for metabolites of chlorogenic acid, such as caffeic acid and ferulic acid.
Chlorogenic acid-induced hormetic biphasic dose responses in a spectrum of experimental designs:
- Responses to direct exposures in a range of cell types;
- Preconditioning experiments in which a prior dose of chlorogenic acid protected against a subsequent stressor agent;
- Studies that included direct exposure, showing hormesis dose responses and then selecting the optimal hormetic dosage as a preconditioning treatment to protect against a subsequent exposure to a toxic agent; and
- A mixed group of experiments in which preconditioning was conducted, including several neuronal cellular models, all showing protection against the subsequent exposure to the toxic agent.
However, in the context of translating experimental data to clinical relevance, the concentrations employed in the majority of the in vitro studies with chlorogenic acid far exceeded transitory peak levels, even in heavy coffee drinkers (i.e., approximately 3 μM). In addition to the use of unrealistically high chlorogenic acid concentrations, exposures were prolonged, ranging from 1 to 3 days. These studies are of limited relevance to humans, a similar concern raised by other researchers involved with polyphenol research.
The present paper has framed the hypothesis that key coffee constituents, such as chlorogenic acid, show hormetic effects in a range of cell types and endpoints. Chlorogenic acid may affect some of the health benefits of coffee drinking via its role in GI tract health and beneficial brain-gut interaction.”
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0009279724004897 “Do the hormetic effects of chlorogenic acid mediate some of the beneficial effects of coffee?” (not freely available) Thanks to Dr. Evgenios Agathokleous for providing copies of this and the following paper.
A 2024 review by the same research group was on hormetic effects of caffeic acid:
“Caffeic acid is a polyphenol present in numerous fruits and vegetables, especially in coffee. Diets contain about 5–10 to 50 milligrams per day of caffeic acid while coffee ingestion provides about another 250–600 milligrams per day. For the moderate to heavy coffee drinker this would result in an ingestion of about 600–1000 milligrams of caffeic acid from food and coffee consumption.
The present paper evaluates whether caffeic acid may act as an hormetic agent, mediating its chemoprotective effects as has been shown for related agents, such as rosmarinic acid, ferulic acid, and chlorogenic acid. Caffeic acid protective effects were mediated via the upregulation of a series of antioxidant enzymes related to activation of Nrf2.
Caffeic acid enhanced the lifespan of C. elegans along with similar observations for rosmarinic acid that can be hydrolyzed to caffeic acid. Several hundred plant-based agents can enhance lifespan in experimental models such as C. elegans, and there is a competition to find the most effective agents with potential commercial applications.
Hormetic effects typically show a 30 to 60% stimulation above control. This is far below the 2 to 3-fold greater than control detection limit for statistical significance based on human variability/bioplasticity and are often reported as false negatives.
A weight-of-evidence approach was proposed based on multiple in vivo and in vitro test results to derive a study design strategy to increase detection of hormetic effects within the clinical trial framework. Such research should explore hormetic based interactions linking protective catabolic-based adaptive responses with activation and regulation of anabolic mediated hormetic growth effects.”
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/19390211.2024.2410776 “Caffeic Acid: Numerous Chemoprotective Effects are Mediated via Hormesis” (not freely available)
A 2024 review provided an overall picture of coffee compounds’ cardiometabolic effects:
“This review provides a comprehensive synthesis of longitudinal observational and interventional studies on the cardiometabolic effects of coffee consumption.
- Findings indicate that while coffee may cause short-term increases in blood pressure, it does not contribute to long-term hypertension risk.
- There is limited evidence indicating that coffee intake might reduce the risk of metabolic syndrome and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
- Coffee consumption is consistently linked with reduced risks of type 2 diabetes (T2D) and chronic kidney disease (CKD), showing dose-response relationships.
- The relationship between coffee and cardiovascular disease is complex, showing potential stroke prevention benefits but ambiguous effects on coronary heart disease.
- Moderate coffee consumption, typically ranging from 1 to 5 cups per day, is linked to a reduced risk of heart failure, while its impact on atrial fibrillation remains inconclusive. Coffee consumption is associated with a lower risk of all-cause mortality, following a U-shaped pattern, with the largest risk reduction observed at moderate consumption levels.
- Except for T2D and CKD, Mendelian randomization studies do not robustly support a causal link between coffee consumption and adverse cardiometabolic outcomes.
Potential beneficial effects of coffee on cardiometabolic health are consistent across age, sex, geographical regions, and coffee subtypes and are multi-dimensional, involving antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, lipid-modulating, insulin-sensitizing, and thermogenic effects. Based on its beneficial effects on cardiometabolic health and fundamental biological processes involved in aging, moderate coffee consumption has the potential to contribute to extending healthspan and increasing longevity.”
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11493900 “Coffee consumption and cardiometabolic health: a comprehensive review of the evidence”