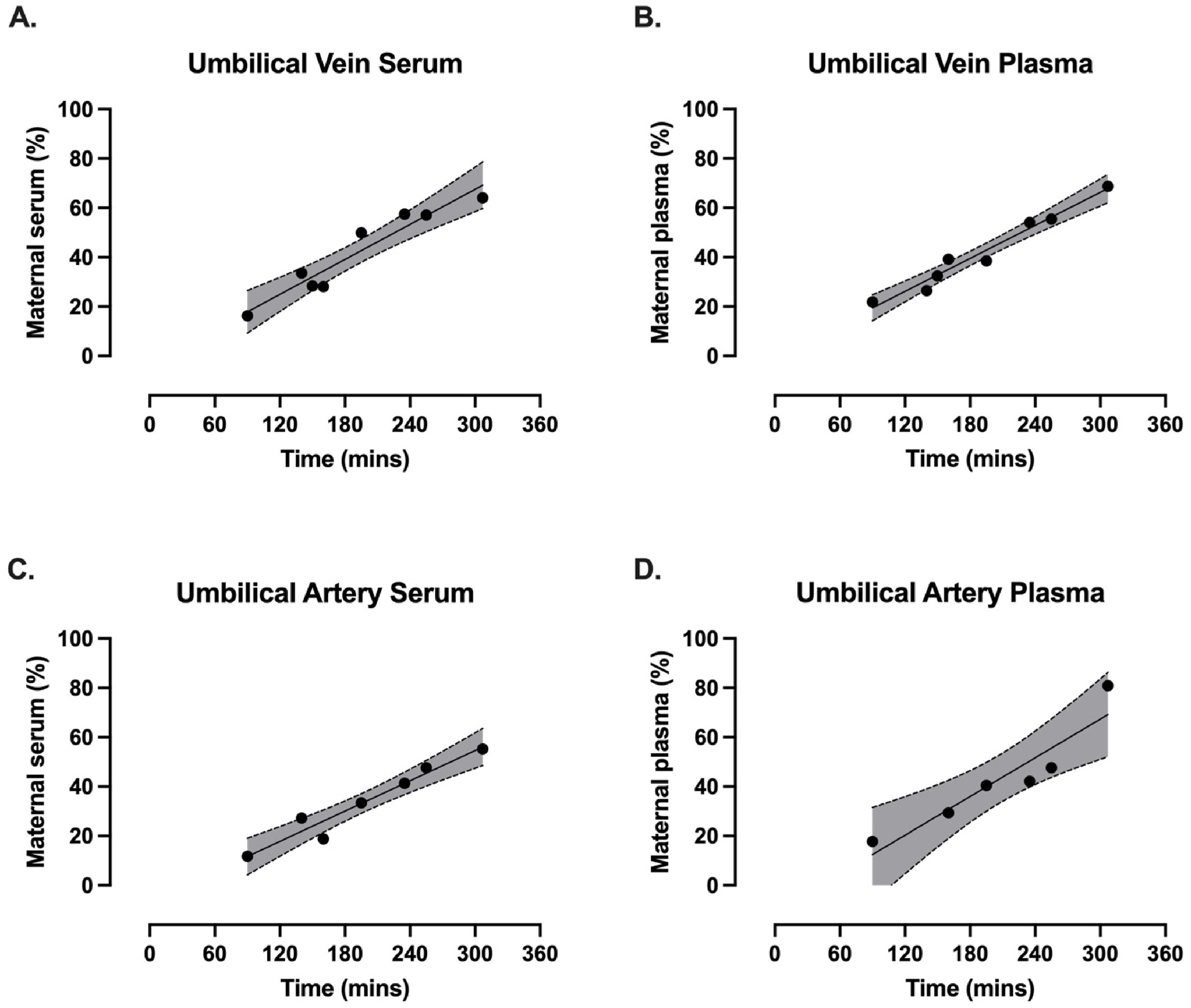
Continuing Plasmalogens Week with three 2025 papers, starting with a human study of plasmalogens’ effects of decreasing breastfed infants’ infections and inflammation:
“Mothers reported on breastfeeding and infant infections in questionnaires collected at 1 month, 3 months, 6 months, 12 months, and 18 months post-birth. Parent-reported infection burden was defined as the total number of infant respiratory tract infections, gastroenteritis, conjunctivitis, and acute otitis media episodes reported by mothers between birth and 6 months for 6-month analyses, and between birth and 12 months for 12-month analyses.
We constructed a causal mediation model to estimate the proportion of effects explained by a direct effect of breastfeeding on inflammation, measured via glycoprotein acetyls (GlycA)—the average direct effect (ADE)—and the proportion that was mediated by metabolomic biomarkers/lipid—the average causal mediation effect (ACME).
Breastfeeding is negatively associated with GlycA, positively associated with plasmalogens, and plasmalogens are negatively associated with GlycA. However, the positive association between breastfeeding and plasmalogens is stronger than the negative direct association between breastfeeding and inflammation, resulting in an ACME that exceeds the total effect. This pattern indicates that plasmalogens may play a dominant role in mediating the relationship between breastfeeding and systemic inflammation.
We have recently developed a plasmalogen score that is associated with a range of cardiometabolic outcomes, including type 2 diabetes and CVD.
- At 6 months, the plasmalogen score was estimated to mediate 162% of the total effect (proportion mediated: 1.62, i.e. average causal mediation effect (ACME) to total effect ratio of 1.62, resulting in a percentage > 100%) of breastfeeding on GlycA.
- At 12 months, the plasmalogen score mediated an estimated 75% of the total effect of breastfeeding on GlycA.
Any breastfeeding, regardless of supplementary feeding, was associated with lower inflammation, fewer infections, and significant, potentially beneficial changes in metabolomic and lipidomic markers, particularly plasmalogens. There was evidence of bidirectional mediation: metabolomic biomarkers and lipids mediated breastfeeding’s effects on inflammation, while inflammation partly mediated breastfeeding’s impact on certain metabolites and lipids.”
https://bmcmedicine.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12916-025-04343-0 “The protective effect of breastfeeding on infant inflammation: a mediation analysis of the plasma lipidome and metabolome”
Reference 48 was the 2024 plasmalogen score study.
A second study by many of the first study’s researchers used the same cohort as the first study to investigate effects of maternal obesity on infant obesity:
“We aimed to investigate associations between maternal pre-pregnancy body mass index (pp-BMI), lipidomic profiles of mothers, human milk, and infants, and early life growth. We were particularly interested in ether lipids as they are higher in breastfed infants compared to formula-fed infants, are enriched in human milk compared to infant formula, and are involved in metabolic health and inflammation in adult populations.
Maternal plasmalogen score was negatively associated with pp-BMI and positively associated with plasmalogens in human milk and infant plasmalogen scores from birth to four years of age. We were unable to establish clear links between plasmalogen score and infant BMI within the first 4 years.
These findings position plasmalogens and ether lipids as potential biomarkers or intervention targets for reducing transmission of obesity from mother to infant. Optimising lipid profiles through reducing maternal pp-BMI and dietary or supplemental ether lipids may represent a novel strategy for mitigating early-life obesity risk.”
https://www.researchsquare.com/article/rs-7089146/v1 “Maternal BMI and infant obesity risk: a lipidomics perspective on the developmental origins of obesity”
There was a lot of hand waving and weasel-wording (i.e., could, may, potential, associated with) but little causal evidence in this preprint. Reference 42 was the preprint version of the first study.
A third paper investigated 9- to 12-year-olds’ plasmalogen levels and molecular types:
“The importance of plasmalogens (Pls) in several cellular processes is known, one of which is their protective effect against oxidative damage. The physiological role of Pls in human development has not been elucidated. This study is the first report on plasmalogen levels and molecular types in children’s plasma.
Ethanolamine plasmalogen (PlsEtn 16:0/20:5) and choline plasmalogen (PlsCho 16:0/20:5), both carrying eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA, ω-3), were significantly lower in girls than in boys. There was no significant difference observed among the 9, 10, 11, and 12-year-old groups between girls and boys in their levels of PlsEtn 16:0/20:5. However, a significant decrease in the levels of PlsCho 16:0/20:5 was observed for 9, 10 and 12-year-old groups of girls compared to boys.
- In both sexes, the plasmalogen levels for the 12-year-old children were lower than those for the 9-year-old children.
- PlsCho (16:0/18:2) linoleic acid (ω-6)-derived was lower in the overweight children than in the normal-weight children for both sexes.
- Arachidonic acid (ω-6)-containing PlsEtn (18:0/20:4) was the most abundant ethanolamine-type plasmalogen in both sexes.
This study has many limitations as follows:
- Non-fasting plasma samples were collected from the children’s plasma and used for analysis; since diet can influence Pls levels, the result may be affected by the sample collection method.
- Physical activity was also not monitored, which could have an influence on plasma levels, and
- A limited number of plasmalogen molecular species were quantified in this study.
A follow-up study may be essential to determine the plasma Pls in the same population when they are adolescents.”
https://www.mdpi.com/2075-4418/15/6/743 “Application of Liquid Chromatography/Tandem Mass Spectrometry for Quantitative Analysis of Plasmalogens in Preadolescent Children—The Hokkaido Study”