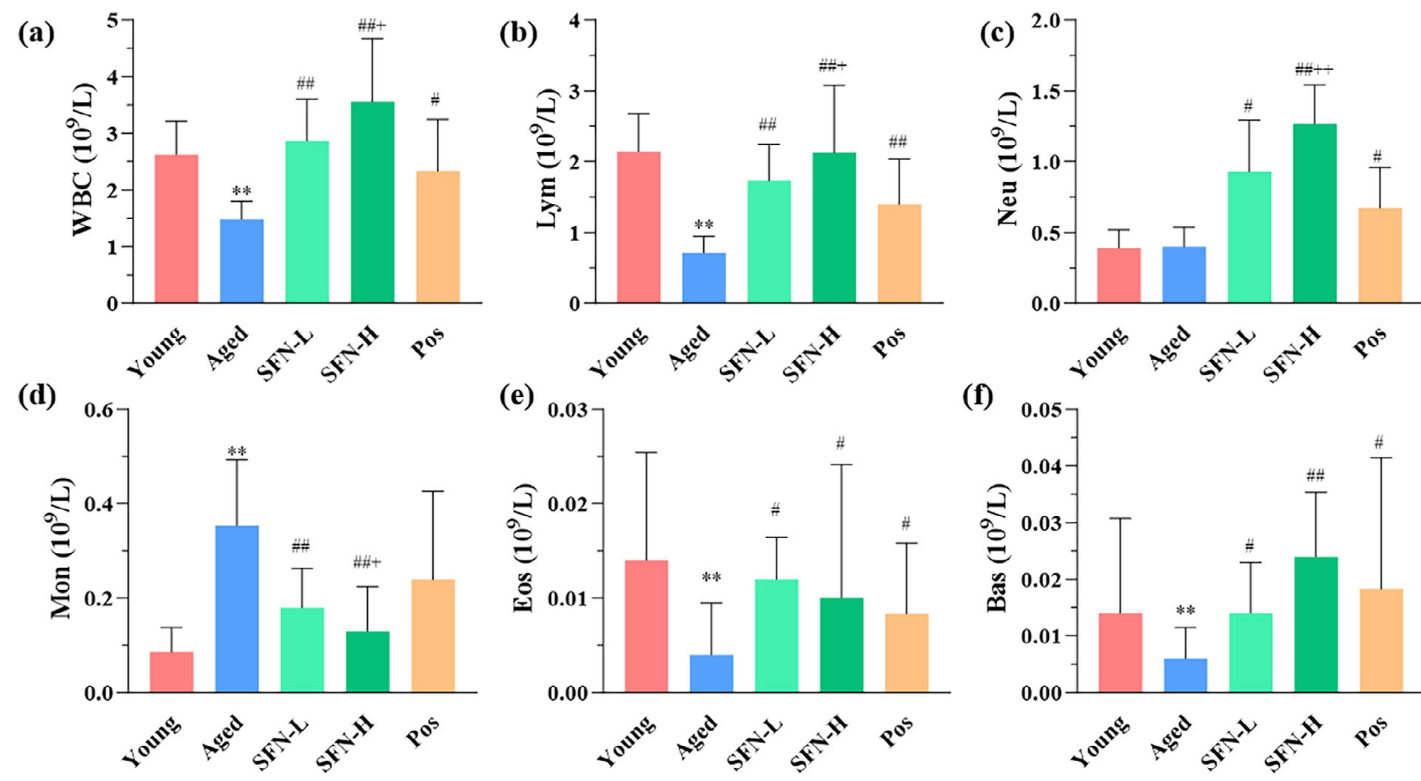
A 2025 clinical trial with old people compared NRF2 effects of acute exercise with pre- and post-exercise sulforaphane treatment:
“This study tested the hypothesis that combining acute exercise (in vivo stimulus) with ex vivo sulforaphane (SFN) treatment would induce greater NRF2 activation and signaling in older adults compared to either treatment alone. This approach was used to bypass the potential issue of inter-individual variability in metabolism and bioavailability of SFN supplementation through oral consumption and thereby provide more rigorous biological control to establish mechanistic feasibility.
Twenty-five older adults (12 men, 13 women; mean age: 67 ± 5 years) performed 30-min cycling exercise. Blood was drawn before and immediately after exercise to isolate peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and incubate with and without SFN (5 μM) treatment.
Acute exercise induced modest transcriptional changes across the four tested transcripts compared to the robust upregulation elicited by SFN. This disparity was notable given the comparable NRF2/ARE binding activity observed between EX and SFN.
Near-significant trends were observed for EX in heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), NAD(P)H quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1), and glutathione reductase (GR) (after Bonferroni correction), while glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit (GCLC) was not induced by EX. In contrast, SFN alone robustly induced expression of NQO1, HO-1, GR, and GCLC.
We had chosen 5 μM as the dose based on pilot data from our laboratory and existing literature from in vitro experiments. However, typically, SFN is not combined with another stimulus.
To test this speculation, we ran a post hoc dose–response experiment where we stimulated PBMCs (n = 5) at six different SFN concentrations ranging from 0 to 20 μM (incubated for 5 h) and analyzed responses across the four genes used in the present study. The dose responses displayed hormetic curves for NQO1, GR, and GCLC, with 5 μM eliciting the peak response, suggesting that the lack of difference between SFN and the combined treatment was due to a ceiling effect of the SFN dose. Interestingly, HO-1 displayed a linear/curvilinear response with the maximal observed response at 20 μM.
In future ex vivo studies, a sulforaphane concentration of 1–2 μM in combination with acute exercise is predicted to enhance the expression of these antioxidant genes in the PBMCs of older adults to a greater extent than either treatment alone. Furthermore, lower SFN plasma concentrations are more likely to be achievable with oral supplementation.
To our knowledge, this is the first trial to measure responses to acute exercise combined with sulforaphane stimulation on NRF2 signaling in older men and women. We did not observe any statistically significant differences in any of our outcome variables between men and women.
Our results demonstrate that combining acute exercise with a sulforaphane stimulus elicits a greater response in nuclear NRF2 activity in older adults. While the response in gene expression did not completely mirror the response in NRF2 activation, it is important to note that NRF2 induces hundreds of cytoprotective genes. The four transcripts we measured are among those most commonly used to represent NRF2 signaling but do not capture the full picture. Full transcriptomics in future studies would address this question.”
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11357-025-01939-5 “Sulforaphane improves exercise-induced NRF2 signaling in older adults: an in vivo-ex vivo approach” (not freely available) Thanks to Dr. Tinna Traustadóttir for providing a copy.
I asked two questions, and will follow up with replies:
- Did a second experiment test effects of these subjects eating broccoli sprouts prior to acute exercise? The clinical trial’s NCT04848792 Study Overview section indicated that was the researchers’ intent.
- What studies have the data that produced this study’s graphical abstract’s younger vs. older NRF2 response graph?