Two more papers cited Precondition your defenses with broccoli sprouts, starting with a 2024 review of broccoli compounds’ influences on autophagy and cellular function:
“Promotion of autophagy has been related to lifespan expansion, tumor suppression, and maintenance of metabolic health. Alterations in this pathway have been related to human diseases or pathological states including neurodegenerative diseases, stroke, metabolic alterations, or cancer.
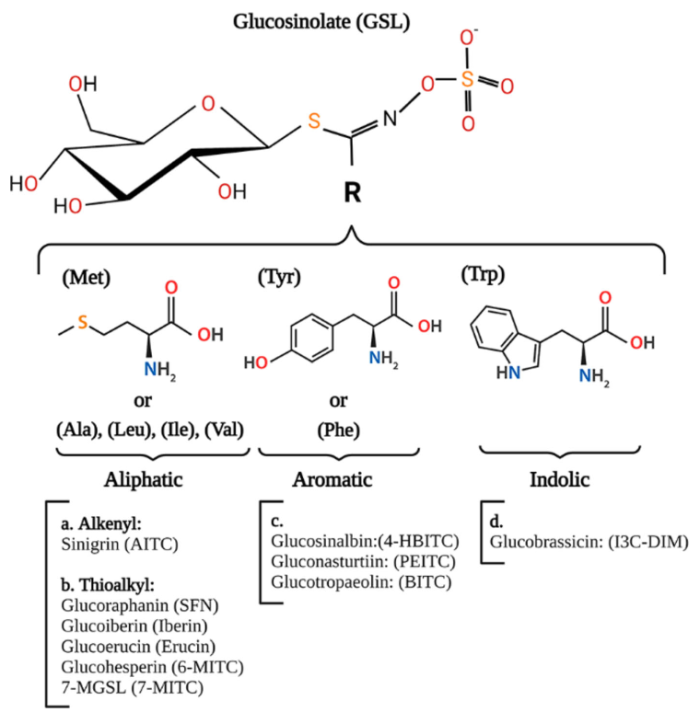
We describe the different types of glucosinolates (GSL), grouped depending on the structure of their side chain, with special attention to those GSL and their derived isothiocyanate (ITC) which have been suggested to be of relevance to treat or prevent human diseases, their structure, and plant source.
It has been shown that SFN activates TFEB, boosting expression of genes required for autophagosome and lysosome biogenesis. SFN induced a short burst of ROS necessary for TFEB activation, and TFEB activity was required for SFN-induced NRF2 activation and protection against acute and chronic oxidative stress.
TFEB was also required for SFN-induced removal of excessive mitochondrial ROS, indicating an important role for mitophagy in SFN-induced antioxidant response. Thus, direct activation of NRF2 by SFN or other ITC can promote autophagy.
Research on autophagy has been characterized by controversies regarding autophagy mediating survival or cell death, or its role in health and disease, not only because autophagy is a complicated process with context dependent roles depending on the cell type or the step of the autophagic pathway being modulated, but also, because in occasions, autophagy is not measured correctly.
An interesting area of research would be to decipher effects of NRF2-regulated or NRF2-independent autophagy induction by ITC, and whether these effects would determine the role of the autophagic process in cellular survival or death. Also, it is needed to clarify which of the effects regulated by ITC are mediated by autophagy, and which ones are not, and the importance of autophagy induction in the therapeutic effects mediated by ITC.”
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11101-024-09944-w “Glucosinolates, isothiocyanates, and their role in the regulation of autophagy and cellular function” (not freely available)
This paper’s contact coauthor (who provided access to the full paper) is also the contact for Our model clinical trial for Changing to a youthful phenotype with broccoli sprouts.
The coauthors of Exercise substitutes? published a 2024 human cell study:
“While physical activity is an excellent inducer of mitochondrial turnover, its ability to ubiquitously activate and enhance mitochondrial turnover prevents definitive differentiation of the contribution made by each pathway. We employed three agents which are activators of important biological markers involved in antioxidant signaling, mitochondrial autophagy, and mitochondrial biogenesis.
Results suggest that early time points of treatment increase upstream pathway activity, whereas later time points represent increased phenotypic expression of related downstream markers. Findings suggest that spatiotemporal progression of these mechanisms following drug treatment is another important factor to consider when examining subcellular changes towards mitochondrial turnover in muscle.”
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2666337624000398 “Sulforaphane, Urolithin A, and ZLN005 induce time-dependent alterations in antioxidant capacity, mitophagy, and mitochondrial biogenesis in muscle cells”
