Four 2023 papers that cited Part 1, starting with a review of hypothetical parameters for taurine clinical trials that aren’t going to happen because:
- Drug companies can’t make money from a research area that’s cheap, not patentable, and readily accessible.
- Government sponsors are likewise not incentivized to act in the public’s interest per their recent behavior.
“We propose the rationale that an adequately powered randomized-controlled-trial (RCT) is needed to confirm whether taurine can meaningfully improve metabolic and microbiome health, and biological age.
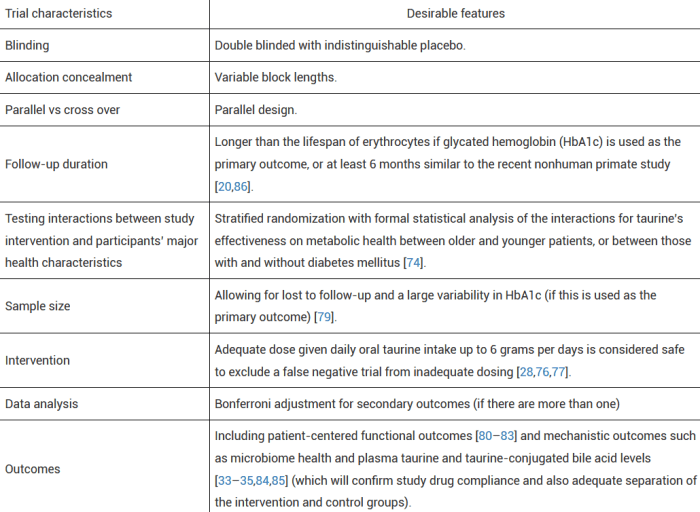
Using long-term survival as a primary outcome is desirable but difficult; any demonstrable difference in this outcome will require a substantial sample size with prolonged follow-up (e.g., 5 years or longer) if the effect size is relatively small (or modest at best). Biological age based on DNA methylation biomarkers according to the Levine PhenoAge or newer biological age models is increasingly being recognized as an important dynamic health parameter, and hence it can also be used as a surrogate outcome in assessing benefits of taurine supplementation.
The recent taurine trial on nonhuman primates used an equivalent dose that was between 3 and 6 g per day for an 80-kg person, and this could represent a reasonable dose range for any human RCTs. We believe that a 6-month or longer interventional period matching what was successfully done on nonhuman primates will be an acceptable time frame in assessing potential efficacy of taurine on human metabolic health in a RCT.”
https://www.sciopen.com/article/10.26599/1671-5411.2023.11.004 “Flattening the biological age curve by improving metabolic health: to taurine or not to taurine, that’s the question”
A six-month duration and a 6 grams per day dose were in the above table’s desirable features column, but epigenetic clock measurements weren’t included as an outcome. I’d guess that its omission reflected disagreements among coauthors, because the desirability of using epigenetic clocks as surrogate measures of human healthspan and lifespan was mentioned several times.
Another review:
“As described in the first half of this review, recent advances in omics analysis technology have led to research to detect the causative gene of dilated cardiomyopathy. It has been found that rare mutations in the taurine transporter gene contribute to the development of dilated cardiomyopathy in humans. It is unlikely that a taurine-deficient diet is a factor in dilated cardiomyopathy, but taurine intake may have positive cardiovascular effects.
The second half summarizes the relationship between taurine and healthspan and lifespan. It is difficult to summarize the effect of age in whole body taurine content, which may vary in species, strain, sex, and age of animal models. Future human studies will clarify the relationship between dietary taurine intake and healthy life expectancy.”
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1347861323000749 “Taurine deficiency associated with dilated cardiomyopathy and aging”
A human study investigated brain chemicals that fluctuate with our circadian rhythm:
“We conducted a MRS study at 7 T, where occipital NAD content, lactate, and other metabolites were assessed in two different morning and afternoon diurnal states in healthy participants. Salivary cortisol levels were determined to confirm that the experiment was done in two circadian different physiological conditions.
Although no significant differences in NAD+, NADH, and NAD+/NADH were detected between the morning and afternoon sessions, there was a significant variance difference in NAD+/NADH, with a higher variance of NAD+/NADH redox ratio in the morning.
None of the over 30 measured brain metabolites were significantly affected by the circadian rhythm (CR) except for taurine, which decreased in the afternoon. Further CR studies should consider the prospective measurement of taurine levels in different regions of the human brain, and explore how taurine supplements could impact brain CR metabolism in health and diseases.”
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphys.2023.1285776/full “Effect of circadian rhythm on NAD and other metabolites in human brain”
I omitted findings regarding this study’s pathetic Balloon Analogue Risk Task (BART) test. Older studies that drew spurious findings from this video game include:
- Who benefits when research promotes a meme of self-sacrifice?
- Who benefits when research with no practical application becomes a politically correct meme?
A rodent study modeled human childhood cataracts:
“Our analysis identified targets that are required for early normal differentiation steps and altered in cataractous lenses, particularly metabolic pathways involving glutathione and amino acids. Glutathione and taurine were spatially altered, and both taurine and the ratio of reduced glutathione to oxidized glutathione, two indicators of redox status, were differentially compromised in lens biology.

Dietary amino acid supplementation has been shown to prevent cataract development, and dietary intake of taurine was protective in a glutathione depletion-derived opacity model. This opens up the possibility that dietary supplementation of taurine could be used as a strategy to prevent human congenital cataracts.
Our findings shed light on molecular mechanisms associated with congenital cataracts, and point out that unbalanced redox status due to reduced levels of taurine and glutathione, metabolites already linked to age-related cataracts, could be a major underlying mechanism behind lens opacities that appear early in life.”
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2213231723002707 “Unbalanced redox status network as an early pathological event in congenital cataracts”
