Here are three 2025 clinical trials of the Nrf2 activator astaxanthin’s effects. Let’s start with a clinical trial of inflammation-related diabetic complications and insulin resistance:
“We investigated effects of 10 mg/day astaxanthin (ASX) supplementation for 12 weeks on microRNAs (miRNAs), lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC), and α-hydroxybutyrate (α-HB) as novel factors in development of a variety of diabetes-related complications.
- LPC is believed to play a significant role in atherosclerosis and inflammatory diseases by modifying functions of multiple cell types, including smooth muscle cells, endothelial cells, monocytes, macrophages, and T cells. LPC can interfere with glucose-stimulated insulin secretion by impairing calcium homeostasis and other signaling pathways that are crucial for the proper functioning of beta cells. This impairment exacerbates hyperglycemia in diabetic patients. LPCs may impede insulin signaling pathways, thereby contributing to insulin resistance (IR).
- α-HB is also an indicator of IR and impaired glucose regulation, both of which appear to result from excessive lipid oxidation and oxidative stress. The European population cohorts in 2016 identified α-HB as a selective biomarker for decreased glucose tolerance and prediabetes, which was independent of age, sex, BMI, and fasting glucose.
- A number of studies have established a link between miR-21, miR-34a, and miR-155 and diabetic complications such as retinopathy and nephropathy.
In the ASX group, participants were divided into 2 subgroups according to the urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio (ACR) (< 30 mg/g or ≥ 30 mg/g, an indicator of diabetic kidney disease).
- The level of fasting plasma glucose before and after 12 weeks of treatment with ASX was 139.27 ± 21.18 vs. 126.43 ± 18.97 (p = 0.002), demonstrating a significant reduction compared to the placebo group.
- In the ASX group, the mean HbA1c level at baseline was 7.89 ± 0.79 and declined to 7.05 ± 0.35 after the supplementation period, which was statistically significant.
- Supplementation with ASX resulted in a statistically significant drop in HOMA-IR levels, whereas this parameter was not altered significantly in the placebo group.
- The ASX group, in comparison with the placebo group, demonstrated marked changes in lipid profile factors such as TC, TG, and LDL (p = 0.011, p = 0.043, and p = 0.022, respectively).
Clinical studies indicate that rigorous diabetes management does not substantially diminish appearance of complications. Modifications in oxidative stress and IR markers, as well as miRNA expression, must be analyzed to identify biological markers with sufficient predictive power for development of complications in diabetic patients.
Supplementation with ASX substantially diminished the levels of α-HB, LPC, and inflammation-related miRNAs in diabetic patients with and without complications.”
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1155/ije/5878361 “Astaxanthin Modulates Inflammation in Type 2 Diabetes via Regulation of microRNAs, Lysophosphatidylcholine, and α-Hydroxybutyrate”
Another clinical trial investigated astaxanthin’s effects in heart failure patients:
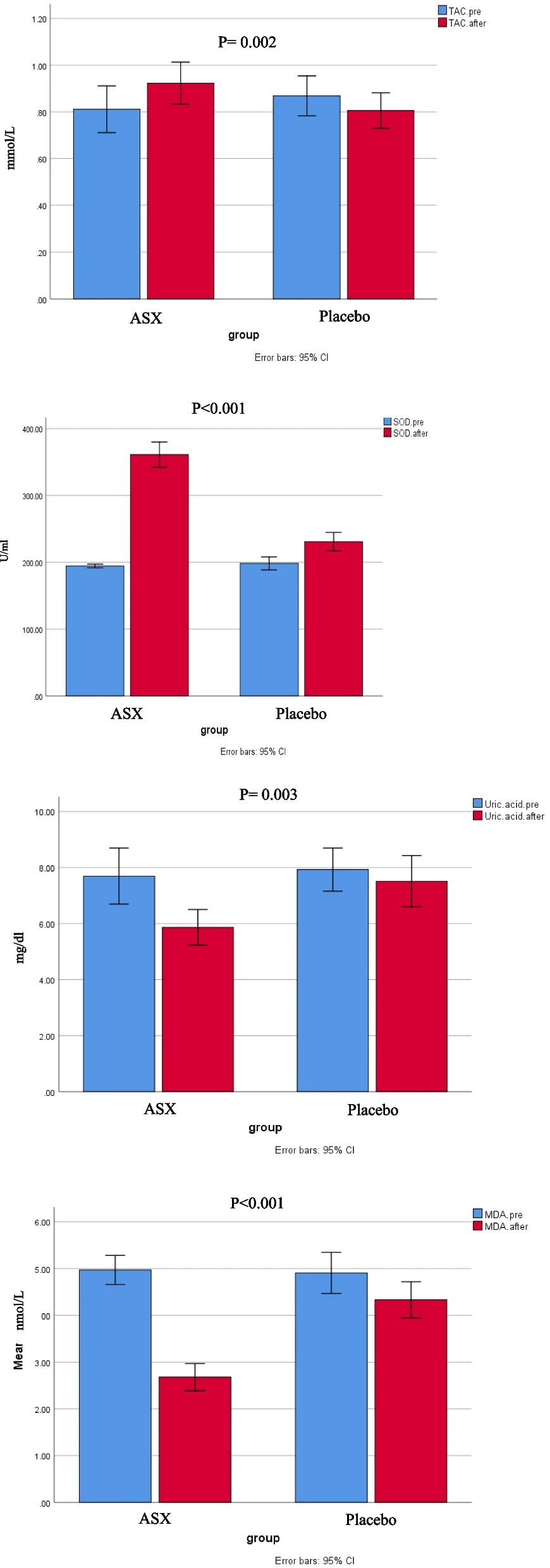
“Chronic heart failure (HF) is often linked to increased oxidative stress and metabolic issues like high uric acid, which can worsen outcomes.This study aimed to investigate the effects of ASX supplementation on oxidative stress markers as the primary outcome and clinical symptoms in patients with HF.
80 patients with HF were enrolled and randomly assigned to receive either ASX (20 mg/day) or a placebo (20 mg/day of maltodextrin) for 8 weeks. Biomarkers including total antioxidant capacity (TAC), malondialdehyde (MDA), superoxide dismutase (SOD), serum uric acid (UA), and clinical symptoms (dyspnea, fatigue, appetite) were assessed pre-and post-intervention.
Daily supplementation with 20 mg of ASX for eight weeks in patients with HF resulted in significantly greater improvements in oxidative stress biomarkers compared to placebo group. This improvement included reductions in uric acid and MDA, along increases in TAC and SOD.
In our study, participants received the cis-isomer form of ASX. The cis-isomer of ASX demonstrates greater anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties than the trans-isomer, along with enhanced bioavailability. Inconsistencies among studies may be attributed to differences in participants’ baseline antioxidant status, underlying medical conditions, dosage, isomeric form and formulation of ASX used, and the duration of intervention.
One of the strengths of this study is that it represents the first randomized clinical trial to evaluate the effects of ASX supplementation on oxidative stress markers, UA levels, and clinical symptoms in patients with HF. Additionally, potential confounding factors were controlled as much as possible. However, several limitations were identified, including the relatively short intervention duration, limited sample size, limited generalizability of the findings due to the single-center design, absence of blood ASX level measurements, and lack of long-term follow-up.”
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12872-025-05260-z “Impact of astaxanthin on oxidative markers, uric acid, and clinical symptoms in heart failure: a randomized clinical trial”
A third clinical trial evaluated astaxanthin’s effects as an adjunct to standard treatment of community-acquired pneumonia:
“Adult patients diagnosed with community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) were enrolled and assigned to receive either 12 mg/day ASX or a placebo in addition to standard antibiotic therapy for 7 days. Inflammatory markers, including interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), and interleukin-10 (IL-10), were measured at baseline and post-treatment. Secondary outcomes included Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) and Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II (APACHE II) scores.
A total of 80 patients (40 per group) completed the study. Patients receiving ASX exhibited significant reductions in pro-inflammatory cytokines compared to the placebo group. IL-6 and TNF-α levels were significantly lower in the ASX group at the end of the study (P < 0.05). Additionally, SOFA and APACHE II scores showed greater improvements in ASX-treated patients, suggesting a potential role in mitigating disease severity.
These findings suggest that ASX may help preserve organ function, limit the progression of inflammatory injury, and reduce overall disease severity in hospitalized patients with CAP.
ASX is widely regarded as the most potent carotenoid, owing to its unique molecular structure. Its polar-nonpolar-polar configuration enables it to span lipid bilayers and neutralize ROS both within and outside cellular membranes—an advantage not shared by other carotenoids that tend to localize at the membrane surface.
Despite the positive findings of this study, some limitations should nevertheless be considered.
- The relatively small sample size may have limited the statistical power to detect differences in some outcomes and affects the generalizability of the findings.
- Microbiological data on CAP pathogens were not collected. As different microorganisms can trigger distinct inflammatory responses, this limits our ability to assess pathogen-specific variations in ASX efficacy.
- A notable limitation of this study is the short follow-up duration, with outcomes assessed only over a 7-day period. While this timeframe offers insight into the acute effects of ASX on inflammatory and OS markers, it does not clarify whether these benefits are sustained beyond the immediate treatment window.
- The fixed dose of 12 mg once daily may not have maintained optimal therapeutic levels throughout the day. Dose-ranging studies and evaluations of alternative regimens are needed to determine the most effective strategy.”
https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/pharmacology/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1621308/full “The anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of astaxanthin as an adjunctive therapy in community-acquired pneumonia: a randomized controlled trial”
Part 2 continues with four more 2025 human studies of astaxanthin.




There is an interesting connection between astaxanthin and BHT – common food preservative and we know now, created in marine very small organisms. Maybe synergistic or not.
AI result:
Astaxanthin is produced by microalgae such as Haematococcus pluvialis and by certain yeast and bacteria; production is upregulated under stress, including high salinity, nutrient deprivation, and high light, and it protects cells against oxidative damage in these conditions.
BHT is surprisingly also produced naturally by some phytoplankton and cyanobacteria (e.g., Botryococcus braunii and several cyanobacterial species), as well as fungi associated with plants and fruits, suggesting an ecological antioxidant role in small aquatic or microbial organisms.
“No controlled studies or clinical trials were found that test astaxanthin and BHT together as a combined antiviral regimen in humans. The mechanistic complementarity is conceptually interesting: astaxanthin mainly augments host defense and limits oxidative/inflammatory damage, while BHT can directly inactivate enveloped virions by membrane disruption.”
I am getting older enough to start BHT to reduce chances for shingles. For me better than a Shingles shot. Perhaps both astaxanthin and BHT (150mg/day or so) but definitely BHT.